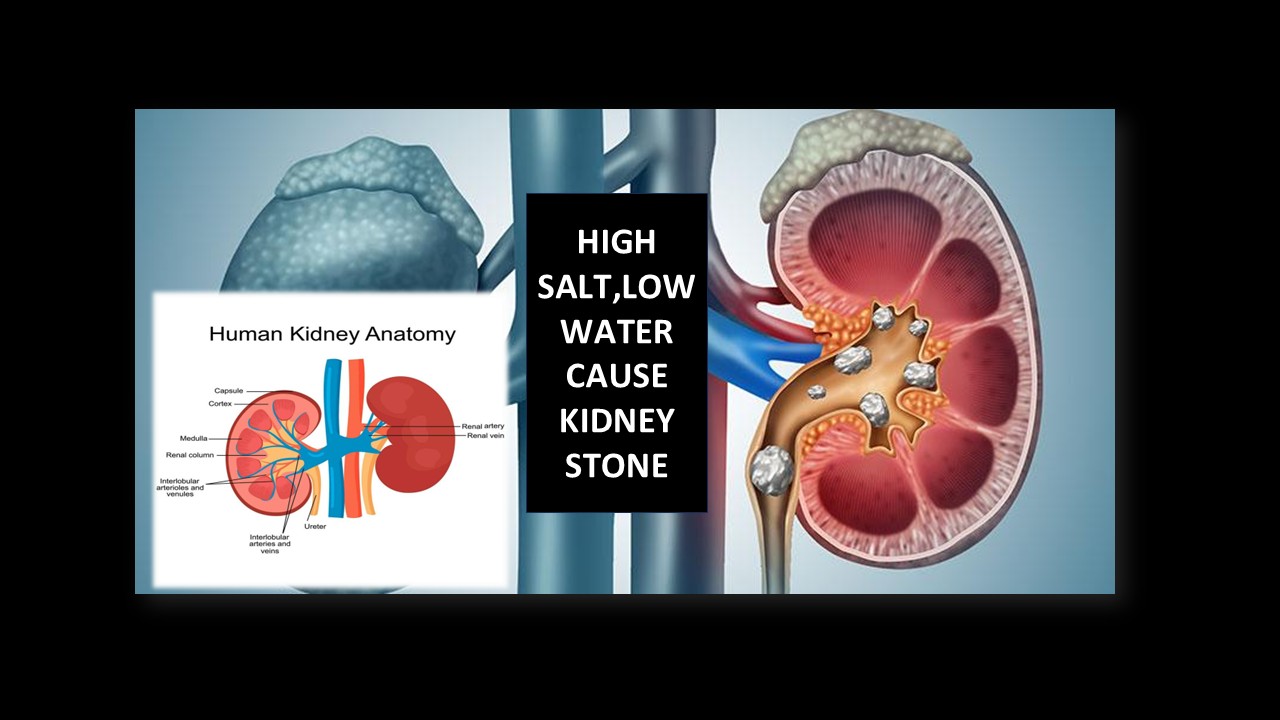
WHAT IS KIDNEY STONE & KIDNEY FAILURE?
IF YOU ARE TAKING HIGH SALT,LOW WATER?
A kidney stone is a solid crystalline mass formed inside the kidney when mineral salts, mainly calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate, precipitate from supersaturated urine.
•When a sudden decline in kidney function occurring over hours to days, leading to reduced urine output and waste accumulation.
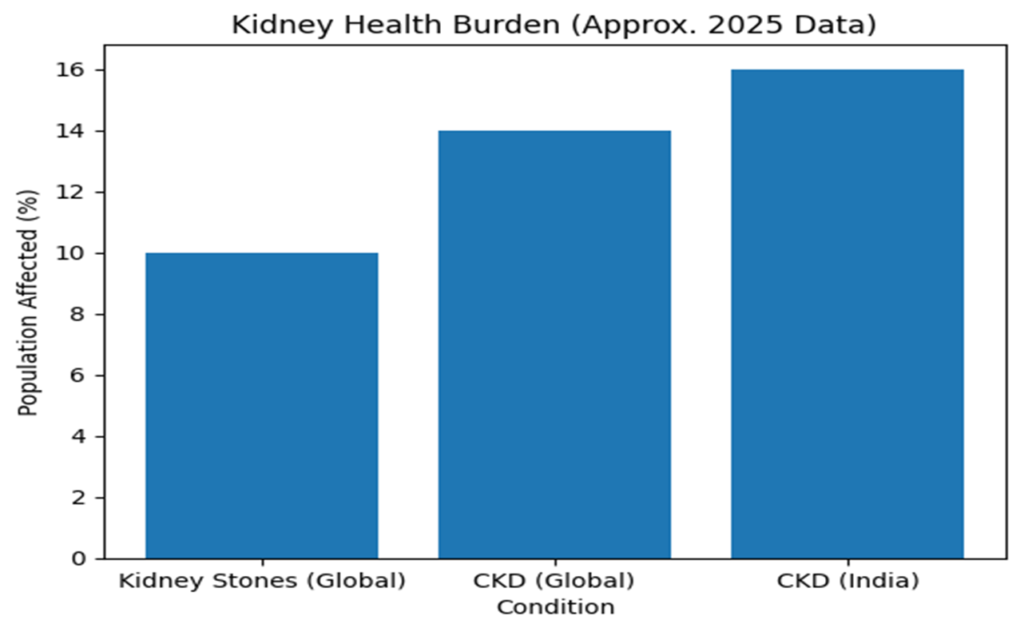
“These values are approximate and based on large-scale population studies available till 2025.”
🧬 WHY KIDNEY STONES FORM?
Recent nephrology research (2024–2025) clearly shows:
•👉 High sodium intake is one of the strongest
dietary risk factors for kidney stones,
especially calcium oxalate stones (most common).
•👉 Low water intake multiplies this
risk by concentrating urine.
•This is clinically proven, not theory.
HOW HIGH SALT CAUSES KIDNEY STONES ?
🧂 1. Sodium–Calcium Link (MOST IMPORTANT)
•High salt intake → ↑ sodium in renal tubules
•Sodium reabsorption in kidney ↓
•As sodium excretion ↑ → calcium excretion also ↑
📌 Scientific fact:
•Sodium and calcium reabsorption
•are linked in renal tubules.
🔥 RESULT:
•Excess calcium enters urine (hypercalciuria)
•Calcium combines with oxalate or phosphate
•Stone crystals start forming
2. ROLE OF LOW WATER INTAKE
Low water intake causes:
•↓ urine volume
•↑ urine concentration
•↑ supersaturation of calcium, oxalate, uric acid
📌 Key concept:
•Stones form when urine becomes supersaturated.
•Without enough water:
👉 crystals cannot be diluted
👉 they aggregate → stones grow
📊 RECENT DATA :
Recent large-scale studies show:
•People with high salt diets have 30–50% higher risk of kidney stones
• Increasing water intake to produce >2.5 L urine/day reduces stone recurrence by ~50%
• Recurrent stone formers often show chronic low-grade dehydration
•👉 These findings are consistent across PubMed & nephrology journals.
EFFECTS OF KIDNEY STONES (BIOLOGY + CLINICAL)
🩺 Short-Term Effects
•Severe flank pain (renal colic)
•Blood in urine (hematuria)
•Nausea & vomiting
•Urinary obstruction
🧠 Biological Impact
•Back-pressure on kidney
•Reduced filtration
•Acute kidney injury (if untreated)
🧬 Long-Term Effects
•Recurrent stones damage renal tissue
•Increased risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD)
•Repeated inflammation of urinary tract
•Permanent reduction in nephron efficiency
📌 Research conclusion:
•Kidney stones are not just painful — they are a marker of disturbed renal physiology.
🔗 STRONG LINK WITH SALT + LOW WATER
•High salt intake causes:
✔ Increased urinary calcium
✔ Increased stone-forming ions
•Low water intake causes:
✔ Concentrated urine
✔ Crystal aggregation
•👉 Together they create ideal conditions for kidney stone formation.
PREVENTION — BIOLOGY-PROVEN
•✅ Adequate hydration
•Maintain dilute urine
•Flush stone-forming ions
•✅ Low sodium diet,LOW SALT INTAKE
•Reduces calcium loss in urine
•✅ Maintain urinary citrate
•Fruits, vegetables, lemon water
•📌 This restores renal homeostasis.